TLS/JA4指纹原理/获取/解析/风控实现与对抗
TLS
TLS:传输层安全协议
wireshark捕获

ip.sec == 10.0.248.173(自己的局域网ip) and ip.addr == 23.37.116.221(目标ip,可能不止一个,负载均衡) and ssl.handshake.type == 1(选择握手包)
多ip:
ip.addr in {202.96.134.133, 104.123.206.140, 23.44.54.118}
Client Hello
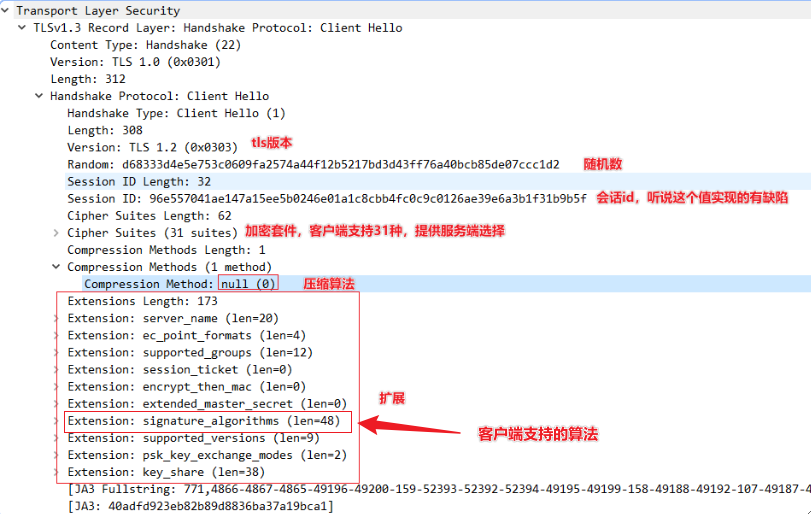
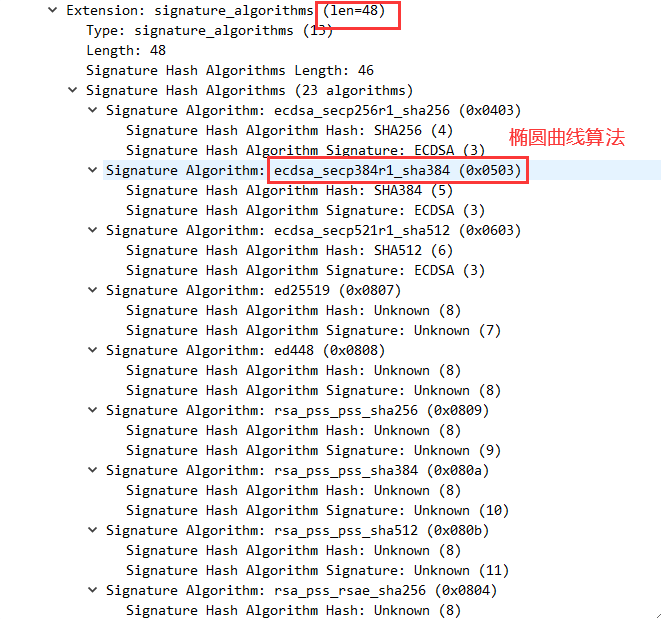
tls包解析
wireshark/tshark保存数据包后,通过pyshark即可读取获取tls包详情,或者对tls包的字节流进行定制化解析。
def is_grease_value(value):
return (value & 0x0f0f) == 0x0a0a
def parse_client_hello(client_hello):
client_hello_bytes = bytes.fromhex(client_hello.replace('\n', '').replace(' ', ''))
tls_version = int(client_hello_bytes[9:11].hex(), 16)
session_id_length = client_hello_bytes[43]
cipher_suite_start = 44 + session_id_length
cipher_suite_length = int.from_bytes(client_hello_bytes[cipher_suite_start:cipher_suite_start+2], 'big')
cipher_suites = []
for i in range(0, cipher_suite_length, 2):
cipher_suite = int.from_bytes(client_hello_bytes[cipher_suite_start+2+i:cipher_suite_start+4+i], 'big')
if not is_grease_value(cipher_suite):
cipher_suites.append(cipher_suite)
compression_method_length = client_hello_bytes[cipher_suite_start + 2 + cipher_suite_length]
extensions_start = cipher_suite_start + 3 + cipher_suite_length + compression_method_length
extensions_length = int.from_bytes(client_hello_bytes[extensions_start:extensions_start+2], 'big')
extensions = client_hello_bytes[extensions_start+2:extensions_start+2+extensions_length]
ext_index = 0
ext_dict = {}
while ext_index < extensions_length:
ext_type = int.from_bytes(extensions[ext_index:ext_index+2], 'big')
ext_len = int.from_bytes(extensions[ext_index+2:ext_index+4], 'big')
ext_content = extensions[ext_index+4:ext_index+4+ext_len]
ext_dict[ext_type] = ext_content
ext_index += 4 + ext_len
return tls_version, cipher_suites, ext_dictJA系列指纹
可通过ja3/ja4的github python SDK+wireshark/tshark数据包直接读ja3/ja4,也可根据tls client hello的字节流进行定制化解析。
需要注意的是,ja3、ja4并不是官方的tls指纹规范,tls握手包中还有其它ja3、ja4没用到的东西,完全可以通过其他内容定制自己的风控指纹。
JA3
ja3明文为加密套件、扩展、椭圆算法的字符串拼接,md5后获得ja3
含义
ja3 fullstring
771,4866-4867-4865-49196-49200-159-52393-52392-52394-49195-49199-158-49188-49192-107-49187-49191-103-49162-49172-57-49161-49171-51-157-156-61-60-53-47-255,0-11-10-35-22-23-13-43-45-51,29-23-30-25-24,0-1-2
771: tls版本号(0x0303是771的十六进制)
4866-4867-4865-49196-49200-159-52393-52392-52394-49195-49199-158-49188-49192-107-49187-49191-103-49162-49172-57-49161-49171-51-157-156-61-60-53-47-255:加密套件,用于协商在通信中使用的加密算法和参数(扩展中的grease为混淆套件,需要从ja3/ja4中剔除)
0-11-10-35-22-23-13-43-45-51:扩展信息,用于提供额外的功能或参数
29-23-30-25-24:椭圆曲线算法的标识符列表,用于在密钥交换中选择椭圆曲线算法
0-1-2:压缩算法的标识符列表,用于协商在通信中使用的压缩算法
ja3
40adfd923eb82b89d8836ba37a19bca1
ja3 fullstring的md5解析
def calculate_ja3(tls_version, cipher_suites, extensions):
ja3_str = f"{tls_version}," + "-".join([str(cs) for cs in cipher_suites]) + "," + "-".join([str(ext) for ext in extensions.keys() if not is_grease_value(ext)])
ec_point_formats = extensions.get(11, b'')
supported_groups = extensions.get(10, b'')
if ec_point_formats:
ec_point_formats_length = int.from_bytes(ec_point_formats[0:1], 'big')
ec_point_formats_list = []
for i in range(0, ec_point_formats_length):
ec_point_format = int.from_bytes(ec_point_formats[i+1:i+2], 'big')
if not is_grease_value(ec_point_format):
ec_point_formats_list.append(ec_point_format)
ec_point_formats_str = "-".join([str(ef) for ef in ec_point_formats_list])
else:
ec_point_formats_str = ""
if supported_groups:
supported_groups_length = int.from_bytes(supported_groups[0:2], 'big') // 2
supported_groups_list = []
for i in range(0, supported_groups_length):
supported_group = int.from_bytes(supported_groups[2+i*2:4+i*2], 'big')
if not is_grease_value(supported_group):
supported_groups_list.append(supported_group)
supported_groups_str = "-".join([str(sg) for sg in supported_groups_list])
else:
supported_groups_str = ""
ja3_str += f",{supported_groups_str},{ec_point_formats_str}"
ja3_hash = hashlib.md5(ja3_str.encode()).hexdigest()
return ja3_str, ja3_hashJA4/JA4_r
ja4_r为加密套件、扩展、签名算法的明文拼接串,ja4为ja4_r分位置的hash。
含义
ja4_r: t13d1516h2_002f,0035,009c,009d,1301,1302,1303,c013,c014,c02b,c02c,c02f,c030,cca8,cca9_0005,000a,000b,000d,0012,0017,001b,0023,002b,002d,0033,4469,fe0d,ff01,0403,0804,0401,0503,0805,0501,0806,0601
(第一部分)
t13d1516h2:
t: tcp/quic
13: tls版本号
d: sni
15: 加密套件长度
16: 扩展长度
h2: http1.1/http2/其它
(第二部分)
002f,0035,009c,009d,1301,1302,1303,c013,c014,c02b,c02c,c02f,c030,cca8,cca9:
加密套件排序(去除grease)
(第三部分)
0005,000a,000b,000d,0012,0017,001b,0023,002b,002d,0033,4469,fe0d,ff01,0403,0804,0401,0503,0805,0501,0806,0601:
扩展排序(去除grease)+逗号+签名算法
ja4: t13d1516h2_8daaf6152771_02713d6af862
t13d1516h2:同上
8daaf6152771:第二部分的sha256前12位
02713d6af862:扩展排序(去除grease)+下划线+签名算法的sha256前12位解析
def get_alpn_protocols(extensions):
alpn_protocols = []
alpn_extension_id = 16 # ALPN extension type is 16 (0x0010)
if alpn_extension_id in extensions:
alpn_data = extensions[alpn_extension_id]
alpn_length = int.from_bytes(alpn_data[0:2], 'big')
alpn_list = alpn_data[2:2+alpn_length]
index = 0
while index < alpn_length:
proto_len = alpn_list[index]
proto_name = alpn_list[index+1:index+1+proto_len].decode('utf-8')
alpn_protocols.append(proto_name)
index += 1 + proto_len
if alpn_protocols[0] == 'h2':
return 'h2'
elif alpn_protocols[0] == 'http/1.1':
return 'h1'
else:
raise Exception(f"Unsupported ALPN protocol: {alpn_protocols[0]}")
def calculate_ja4(tls_version, cipher_suites, extensions, signature_algorithms):
protocol = "t"
if tls_version == 0x301:
tls_version_str = "11"
elif tls_version == 0x302:
tls_version_str = "12"
elif tls_version == 0x303:
tls_version_str = "13"
else:
raise Exception(f"Unsupported TLS version: {tls_version}")
sni = 'd'
cipher_suites_length = len(cipher_suites)
extensions = {k:v for k,v in extensions.items() if not is_grease_value(k)}
extensions_length = len(extensions)
alpn_protocol = get_alpn_protocols(extensions)
ja4_a = f"{protocol}{tls_version_str}{sni}{cipher_suites_length}{extensions_length}{alpn_protocol}"
cipher_suites_str = ",".join([f"{cs:04x}" for cs in sorted(cipher_suites) if not is_grease_value(cs)])
ja4_b_hash = hashlib.sha256(cipher_suites_str.encode()).hexdigest()[:12]
extensions_str = ",".join([f"{ext:04x}" for ext in sorted(extensions.keys()) if not (is_grease_value(ext) or ext in [0x0000, 0x0010])])
signature_algorithms_str = ",".join([f"{sig:04x}" for sig in signature_algorithms])
combined_str = extensions_str + "_" + signature_algorithms_str
ja4_c_hash = hashlib.sha256(combined_str.encode()).hexdigest()[:12]
ja4 = f"{ja4_a}_{ja4_b_hash}_{ja4_c_hash}"
ja4_r = f"{ja4_a}_{cipher_suites_str}_{extensions_str},{signature_algorithms_str}"
return ja4, ja4_r
def get_signature_algorithms(extensions):
signature_algorithms = []
if 13 in extensions:
sig_algorithms = extensions[13]
sig_alg_len = int.from_bytes(sig_algorithms[0:2], 'big') // 2
for i in range(sig_alg_len):
signature_algorithms.append(int.from_bytes(sig_algorithms[2 + 2 * i:4 + 2 * i], 'big'))
return signature_algorithms
def get_ja4(client_hello):
tls_version, cipher_suites, extensions = parse_client_hello(client_hello)
signature_algorithms = get_signature_algorithms(extensions)
ja4_str, ja4_r_str = calculate_ja4(tls_version, cipher_suites, extensions, signature_algorithms)
return ja4_str, ja4_r_strTLS风控实现
基础指纹生成
通过上述代码,变可将握手包字节流解析为客户端各组件详情以及ja3/ja4等,通过tshark+nginx+自定义脚本即可捕获相应指纹并解析。
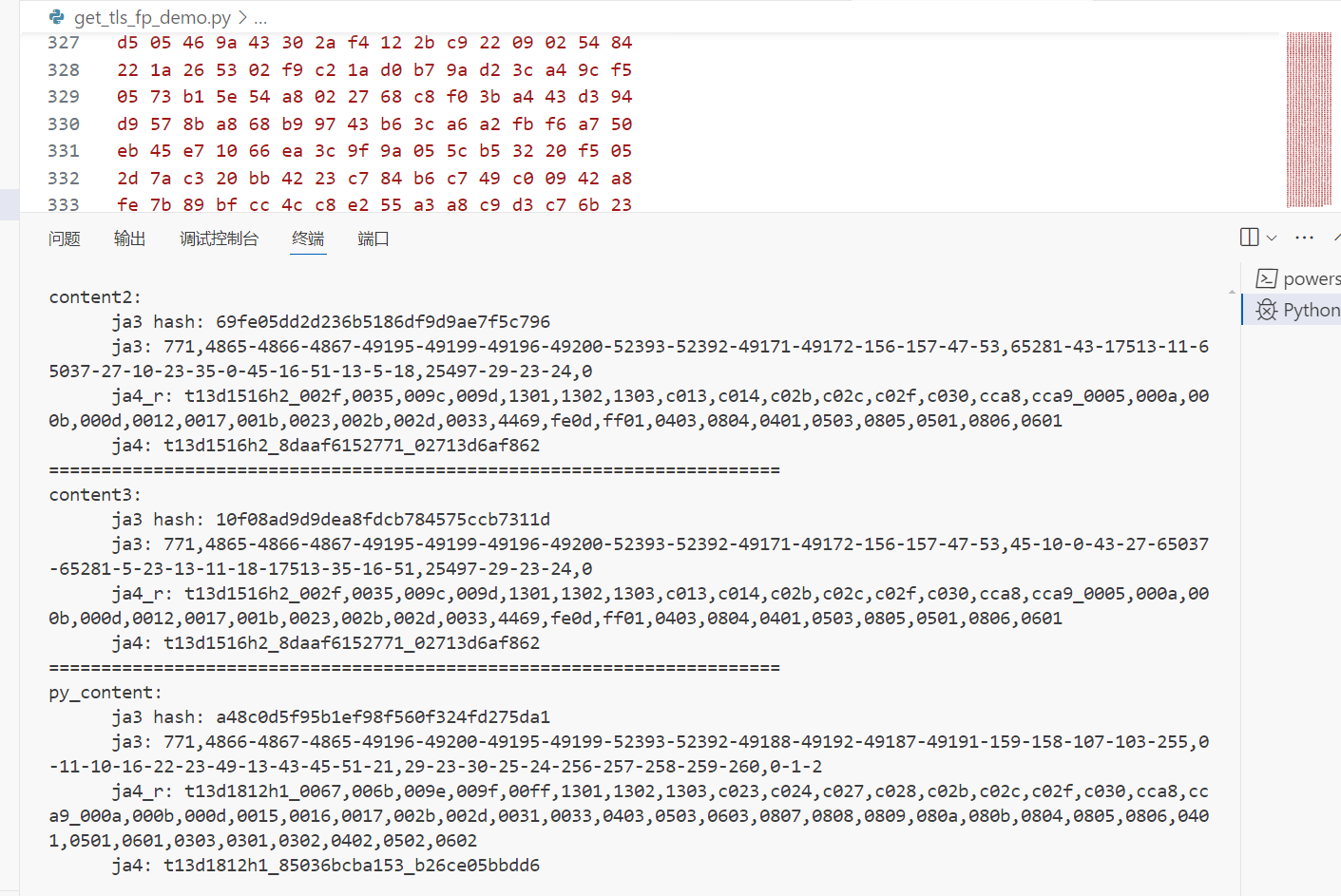
如上图,其中content2和content3为浏览器指纹,py_content为python requests指纹。可以看到,虽然谷歌在12x版本以后随机了加密套件和扩展,并加入了混淆,使得ja3指纹的识别没了作用,但是ja4还是对设备做出有效识别。
浏览器与python tls差别
首先来分析一下http://43.224.225.5:18080/hello的tls检测接口。
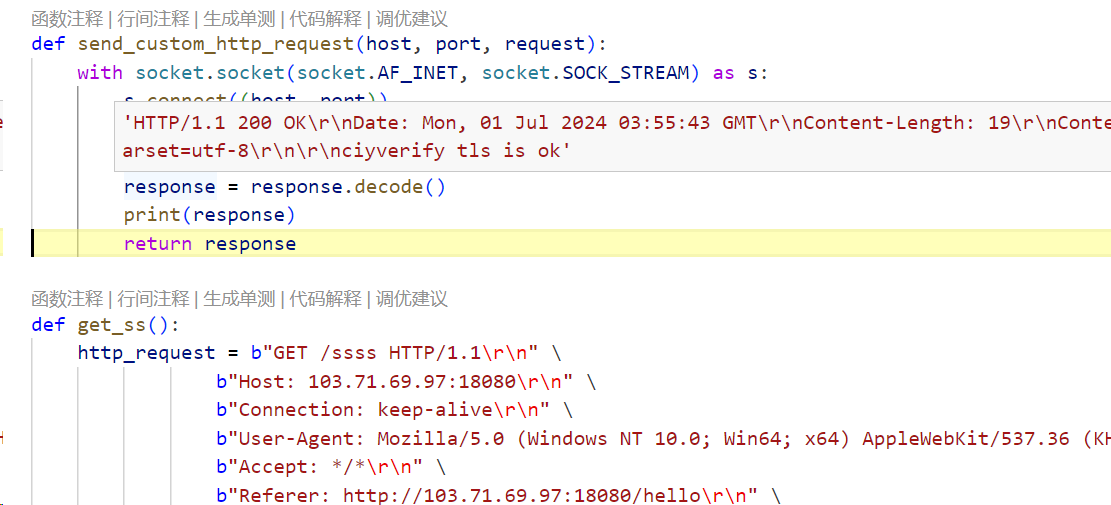
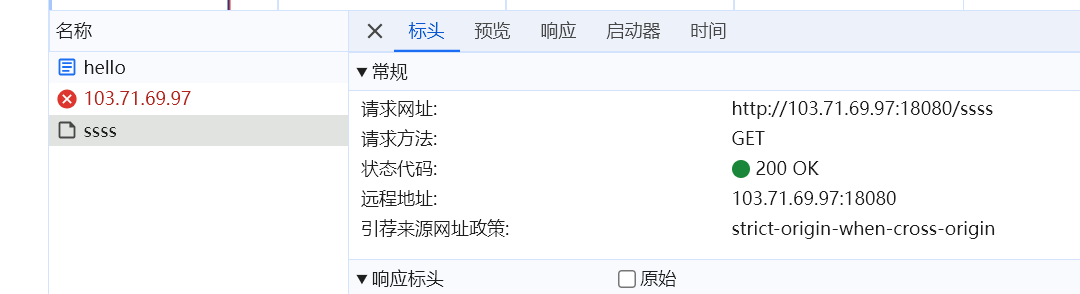 获取tls结果的是一个http请求,显然不是这个。上面请求了https 8443端口,经过测试直接重放ssss结果不通过,先fetch 8443后重放就会通过。
获取tls结果的是一个http请求,显然不是这个。上面请求了https 8443端口,经过测试直接重放ssss结果不通过,先fetch 8443后重放就会通过。
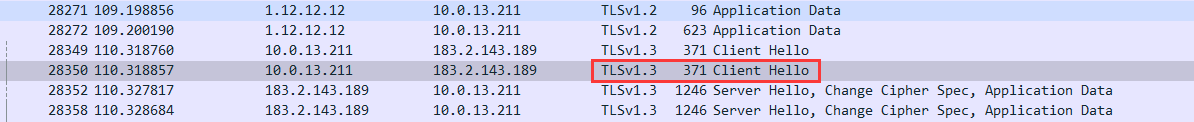
使用tls_client、curl_cffi等第三方包重写流程后发现过不去,打开wireshark抓握手包进行分析。
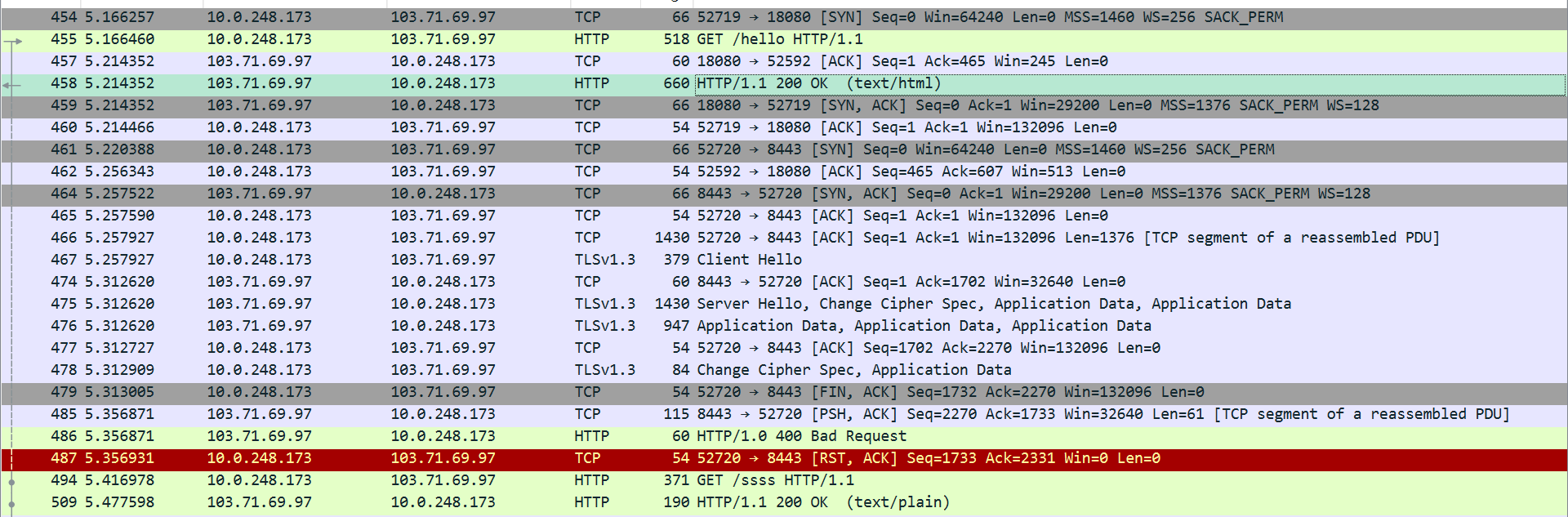
多次对比浏览器和tls_client的client hello发现,虽然ja3随机无法作为识别依据,ja4两者也已经一致,但是tls_client将client hello报文整个发出,而chrome对握手报文进行了分段,导致两者存在明显差别,而谷歌对握手包分段的原因在于扩展长度明显长于tls_client。
继续对比发现差距在于Key Share Entry(密钥交换)扩展,谷歌使用的是x25519+kyber768算法,而tls_client使用的是较为传统的x25519算法,因此握手略有差别。
再扣一些细节的话,python直接请求时,每次握手包的seq(序列号)都是1,而浏览器则是其它值。
另一方面,根据cbb大佬透露在header上也有风控,研究后发现tls_client会将请求头按key的字母顺序进行排序后发送,而谷歌则是按照特定的顺序。
模拟浏览器TLS指纹
cbb大佬的tls测试地址:http://43.224.225.5:18080/hello
通过此测试来验证目前市面上常见的tls指纹解决方案。
浏览器转发
和rpc调用加密接口类似,通过websocket或者插件接收其它语言发送的转发请求,请求返回结果。
python端:
import asyncio
import websockets
import threading
import time
clients = set()
async def handler(websocket, path):
clients.add(websocket)
try:
async for message in websocket:
print(f"Received response: {message}")
# 处理message
finally:
clients.remove(websocket)
async def start_server():
server = await websockets.serve(handler, "localhost", 8765)
await server.wait_closed()
async def send_message():
while True:
time.sleep(0.2)
message = input("Enter message to send: ")
if clients: # Check if there are connected clients
futures = [client.send(message) for client in clients]
await asyncio.gather(*futures)
else:
print("No clients connected")
# 线程启动服务
server_thread = threading.Thread(target=lambda: asyncio.run(start_server()))
server_thread.start()
# 启动发送消息
asyncio.run(send_message())浏览器打开目标网站首页(此用例即为http://103.71.69.97:18080/或者http://103.71.69.97:18080/hello),控制台输入:
const socket = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:8765');
socket.onopen = function() {
console.log('Connected to server');
};
socket.onmessage = async function(event) {
console.log('Message from server: ', event.data);
try {
const result = eval(event.data);
socket.send(JSON.stringify({ success: true, result: result }));
} catch (error) {
socket.send(JSON.stringify({ success: false, error: error.toString() }));
}
};
socket.onclose = function() {
console.log('Disconnected from server');
};
socket.onerror = function(error) {
console.error('WebSocket error: ', error);
};先简单测试下:
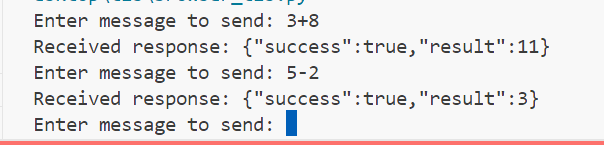
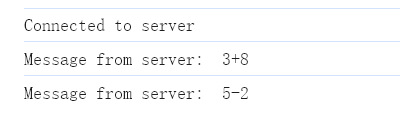
可以看到功能没什么问题,在python端发送以下代码:
try{fetch("https://103.71.69.97:8443/").then(function(){},function(){setTimeout(()=>{window.g = new XMLHttpRequest(); g.open("GET", "http://103.71.69.97:18080/ssss", true);
g.send(); g.onload = function(a){ console.log(g.response); socket.send(g.response); };},100)})}catch{
} 可以看到,借助浏览器可以轻松的突破tls限制。
可以看到,借助浏览器可以轻松的突破tls限制。
需要注意的是,浏览器原生fetch并不支持直接设置代理,所以需要编写插件来实现试下动态传入代理并fetch。
浏览器curl编译
52pojie上某大佬过akamai的做法。
chromium的网络栈相关文档:
https://www.chromium.org/developers/design-documents/network-stack/
主要代码都在src/net下:
 https涉及net/ssl、net/cert等,技术栈不够没有深入研究。
https涉及net/ssl、net/cert等,技术栈不够没有深入研究。
已经有大佬实现了cronet转发,地址:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/I5Xik3ghciSNZ0uju2ID7A
实测可以通过上面的tls检测,但是某些网站的akamai过不去(比如VY航司)。
使用go自定义tls
go的tls包自带功能,网上教程很多,略
socket实现握手
基于上面写到的握手差别,client hello通过修改
https://github.com/boppreh/hello_tls/tree/main/src/hello_tls
进行自定义(主要是names_and_numbers与对应方法实现,,以及syn ack等包实现,kyber使用liboqs实现),请求头顺序直接使用socket写死即可。
代码量有点大,完善后单独开一篇: